Example: Langfuse Prompt Management with Langchain (JS)
Langfuse Prompt Management (opens in a new tab) helps to version control and manage prompts collaboratively in one place.
This example demonstrates how to use Langfuse Prompt Management together with Langchain JS.
const langfuseParams = {
publicKey: "",
secretKey: "",
baseUrl: "https://cloud.langfuse.com",
flushAt: 1 // cookbook-only, send all events immediately
}import {Langfuse} from "npm:langfuse"
const langfuse = new Langfuse(langfuseParams)Simple example
Add new prompt
We add the prompt used in this example via the SDK. Alternatively, you can also edit and version the prompt in the Langfuse UI.
Namethat identifies the prompt in Langfuse Prompt Management- Prompt with
topicvariable - Config including
modelName,temperature labelsto includeproductionto immediately use prompt as the default
For the sake of this notebook, we will add the prompt in Langfuse and use it right away. Usually, you'd update the prompt from time to time in Langfuse and your application fetches the current production version.
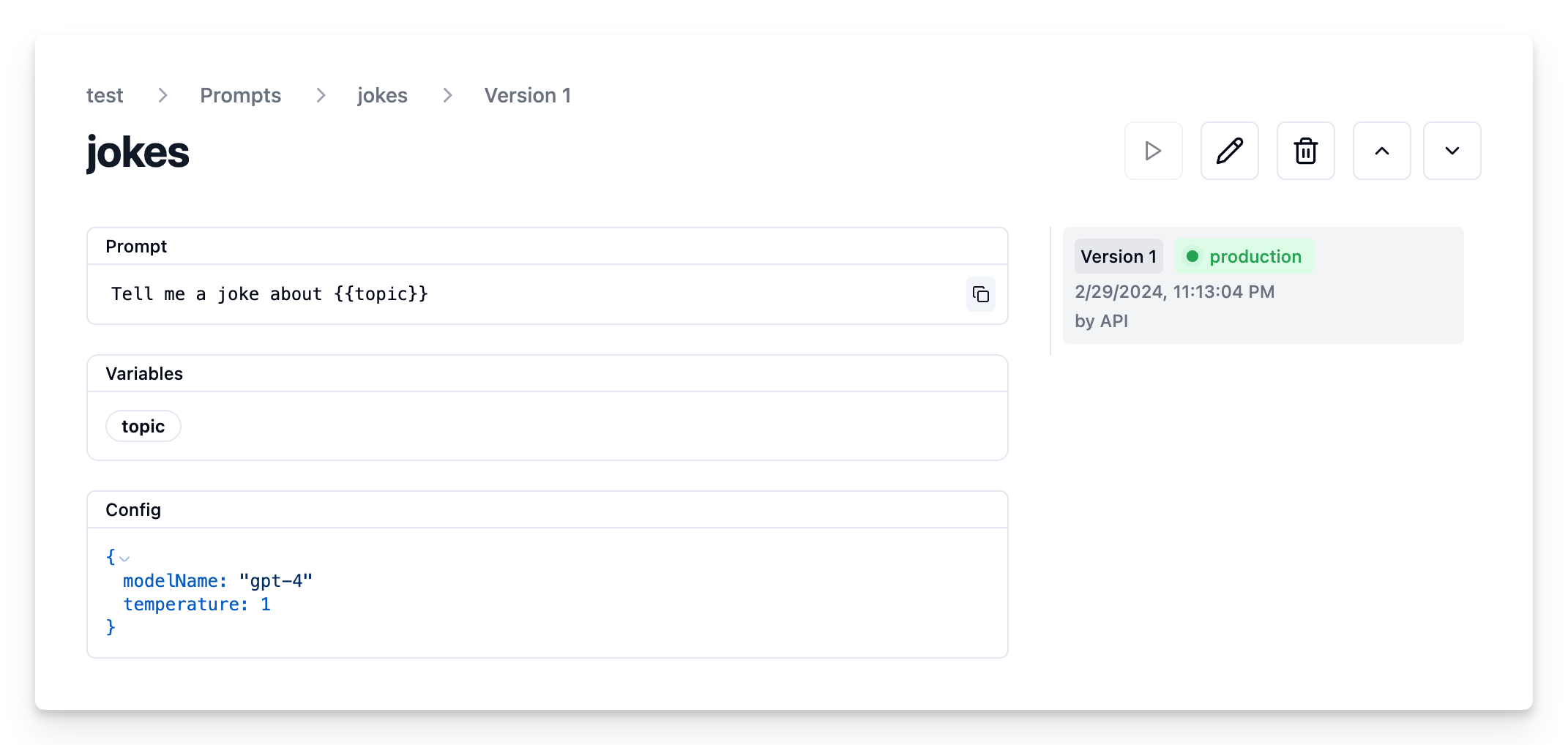
const prompt = await langfuse.createPrompt({
name: "jokes",
prompt: "Tell me a joke about {{topic}}",
config: {
modelName: "gpt-4",
temperature: 1,
}, // optionally, add configs (e.g. model parameters or model tools)
labels: ["production"] // directly promote to production
});Prompt in Langfuse
Run example
Get current prompt version from Langfuse
const prompt = await langfuse.getPrompt("jokes")The prompt includes the prompt string
prompt.prompt[32m"Tell me a joke about {{topic}}"[39mand the config object
prompt.config{ modelName: [32m"gpt-4"[39m, temperature: [33m1[39m }Transform prompt into Langchain PromptTemplate
Use the utility method .getLangchainPrompt() to transform the Langfuse prompt into a string that can be used in Langchain.
Context: Langfuse declares input variables in prompt templates using double brackets ({{input variable}}). Langchain uses single brackets for declaring input variables in PromptTemplates ({input variable}). The utility method .getLangchainPrompt() replaces the double brackets with single brackets.
import { PromptTemplate } from "npm:@langchain/core/prompts"
const promptTemplate = PromptTemplate.fromTemplate(
prompt.getLangchainPrompt()
);Setup Langfuse Tracing for Langchain JS
We'll use the native Langfuse Tracing for Langchain JS (opens in a new tab) when executing this chain. This is fully optional and can be used independently from Prompt Management.
import { CallbackHandler } from "npm:langfuse-langchain"
const langfuseLangchainHandler = new CallbackHandler(langfuseParams)Create chain
We use the modelName and temperature stored in prompt.config.
import { ChatOpenAI } from "npm:@langchain/openai"
import { RunnableSequence } from "npm:@langchain/core/runnables";
const model = new ChatOpenAI({
modelName: prompt.config.modelName,
temperature: prompt.config.temperature
});
const chain = RunnableSequence.from([promptTemplate, model]);Invoke chain
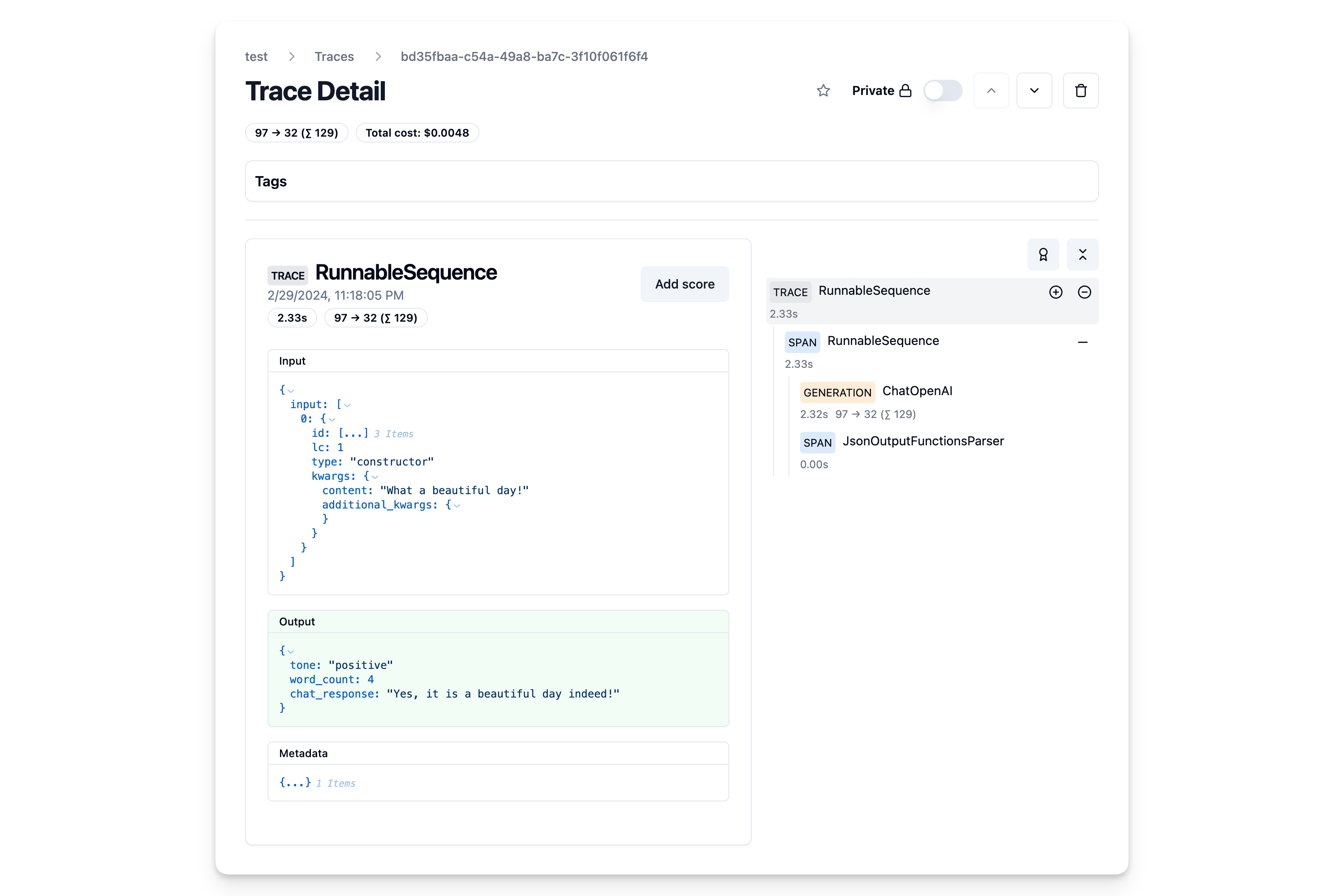
const res = await chain.invoke(
{ topic: "Europe and the Americas" },
{ callbacks: [langfuseLangchainHandler] }
);View trace in Langfuse
As we passed the langfuse callback handler, we can explore the execution trace in Langfuse.
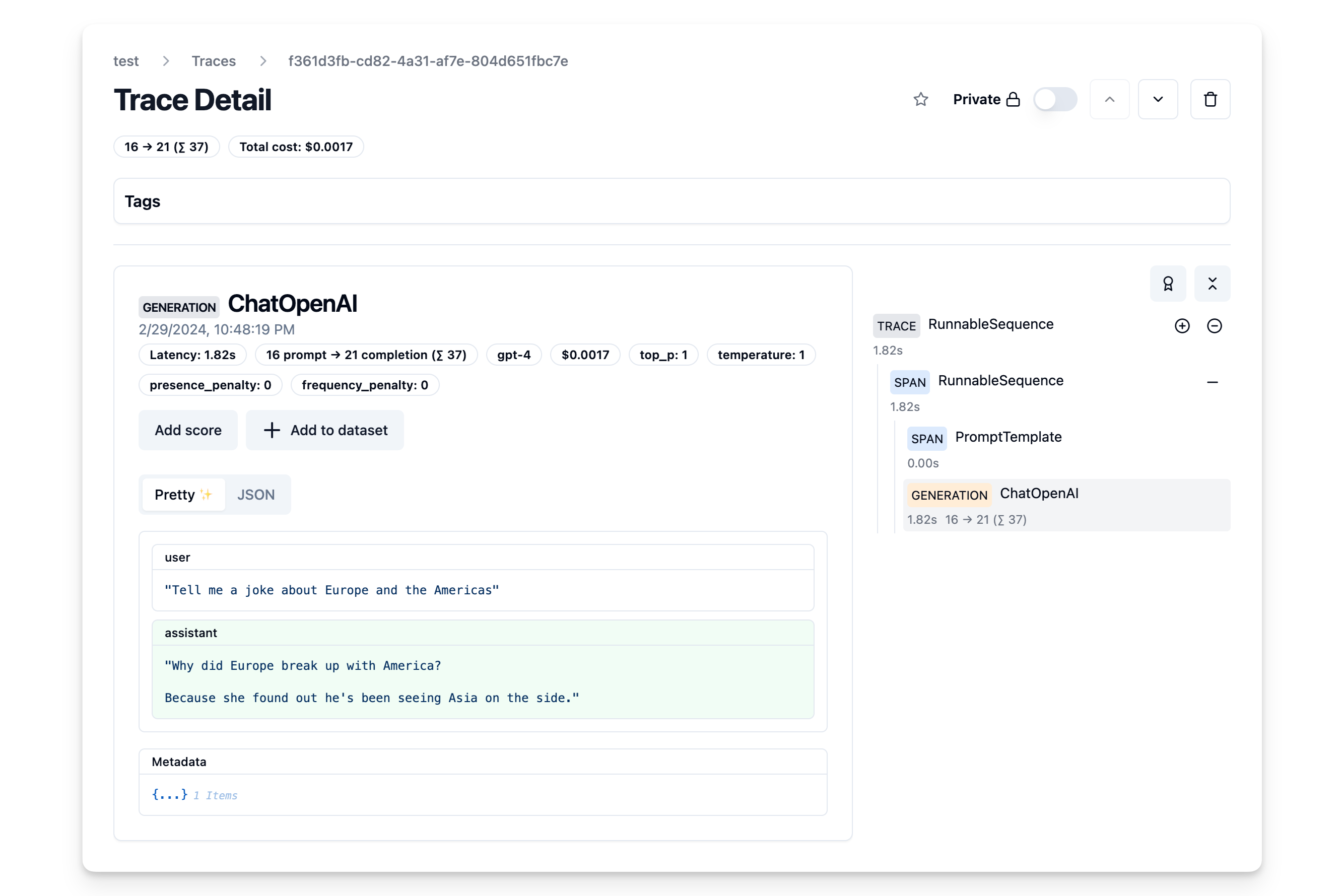
OpenAI functions and JsonOutputFunctionsParser
Add prompt to Langfuse
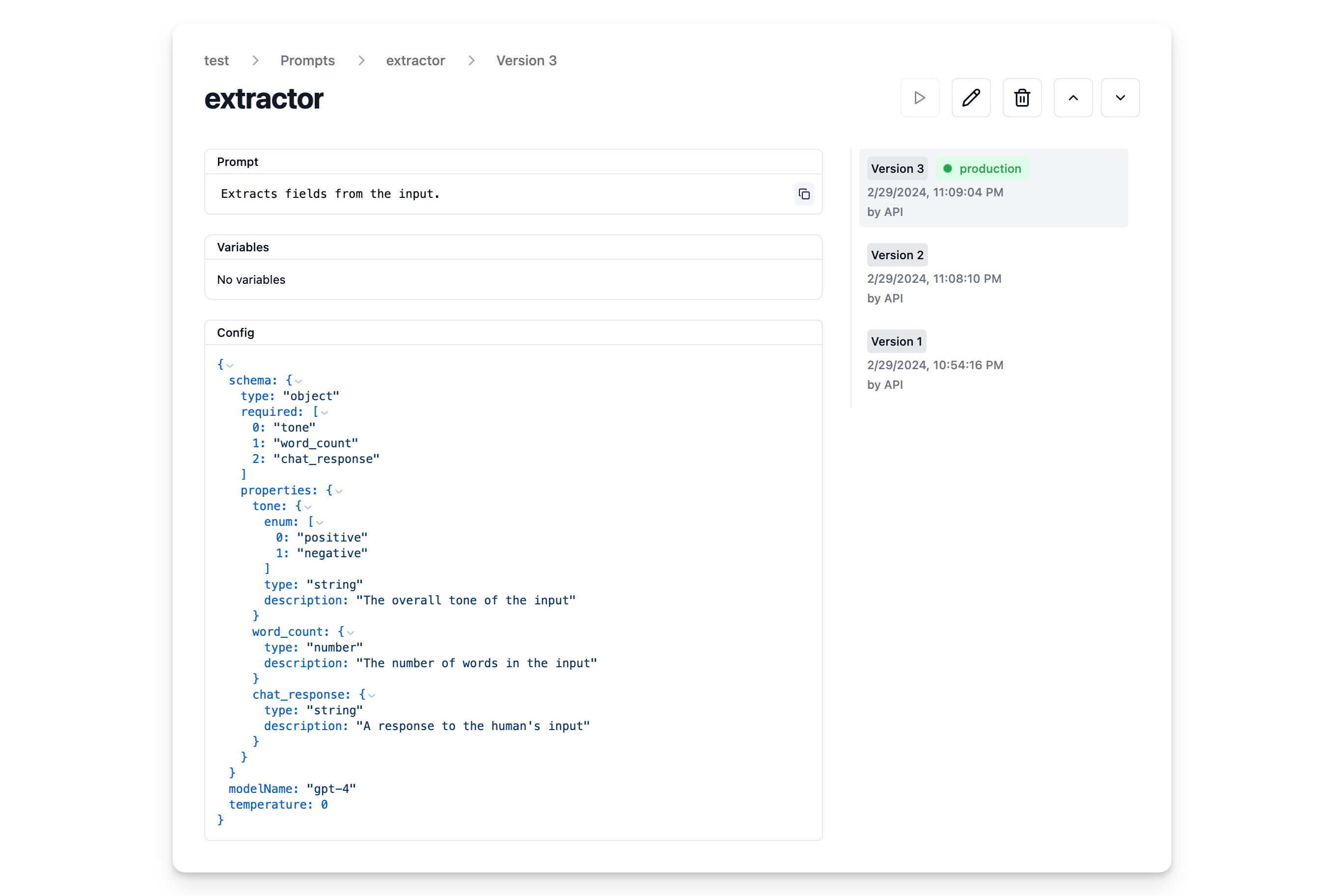
const prompt = await langfuse.createPrompt({
name: "extractor",
prompt: "Extracts fields from the input.",
config: {
modelName: "gpt-4",
temperature: 0,
schema: {
type: "object",
properties: {
tone: {
type: "string",
enum: ["positive", "negative"],
description: "The overall tone of the input",
},
word_count: {
type: "number",
description: "The number of words in the input",
},
chat_response: {
type: "string",
description: "A response to the human's input",
},
},
required: ["tone", "word_count", "chat_response"],
}
}, // optionally, add configs (e.g. model parameters or model tools)
labels: ["production"] // directly promote to production
});Prompt in Langfuse
Fetch prompt
const extractorPrompt = await langfuse.getPrompt("extractor")Transform into schema
const extractionFunctionSchema = {
name: "extractor",
description: prompt.prompt,
parameters: prompt.config.schema,
}Build chain
import { ChatOpenAI } from "npm:@langchain/openai";
import { JsonOutputFunctionsParser } from "npm:langchain/output_parsers";
// Instantiate the parser
const parser = new JsonOutputFunctionsParser();
// Instantiate the ChatOpenAI class
const model = new ChatOpenAI({
modelName: prompt.config.modelName,
temperature: prompt.config.temperature
});
// Create a new runnable, bind the function to the model, and pipe the output through the parser
const runnable = model
.bind({
functions: [extractionFunctionSchema],
function_call: { name: "extractor" },
})
.pipe(parser);Invoke chain
import { HumanMessage } from "npm:@langchain/core/messages";
// Invoke the runnable with an input
const result = await runnable.invoke(
[new HumanMessage("What a beautiful day!")],
{ callbacks: [langfuseLangchainHandler] }
);View trace in Langfuse